Diseases, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 08 junho 2024
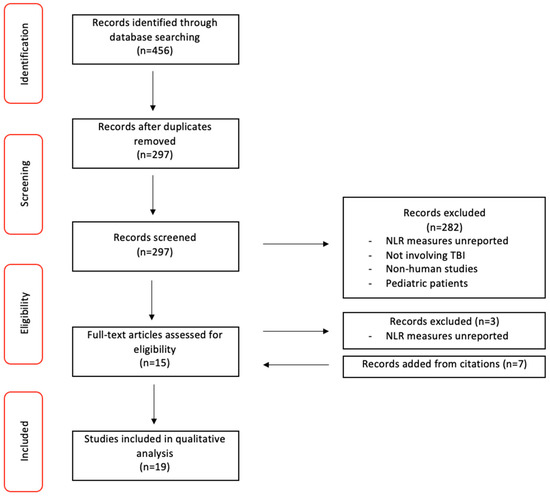
(1) Introduction: Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a leading cause of injury and mortality worldwide, carrying an estimated cost of $38 billion in the United States alone. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) has been investigated as a standardized biomarker that can be used to predict outcomes of TBI. The aim of this review was to determine the prognostic utility of NLR among patients admitted for TBI. (2) Methods: A literature search was conducted in PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science in November 2022 to retrieve articles regarding the use of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) as a prognostic measure in traumatic brain injury (TBI) patients. Inclusion criteria included studies reporting outcomes of TBI patients with associated NLR values. Exclusion criteria were studies reporting only non-primary data, those insufficiently disaggregated to extract NLR data, and non-English or cadaveric studies. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale was utilized to assess for the presence of bias in included studies. (3) Results: Following the final study selection 19 articles were included for quantitative and qualitative analysis. The average age was 46.25 years. Of the 7750 patients, 73% were male. Average GCS at presentation was 10.51. There was no significant difference in the NLR between surgical vs. non-surgical cohorts (SMD 2.41 95% CI −1.82 to 6.63, p = 0.264). There was no significant difference in the NLR between bleeding vs. non-bleeding cohorts (SMD 4.84 95% CI −0.26 to 9.93, p = 0.0627). There was a significant increase in the NLR between favorable vs. non-favorable cohorts (SMD 1.31 95% CI 0.33 to 2.29, p = 0.0090). (4) Conclusions: Our study found that NLR was only significantly predictive for adverse outcomes in TBI patients and not surgical treatment or intracranial hemorrhage, making it nonetheless an affordable alternative for physicians to assess patient prognosis.

Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 - The Lancet
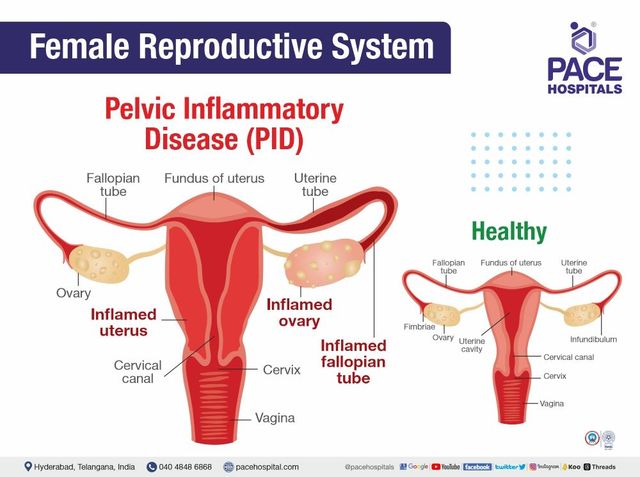
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors
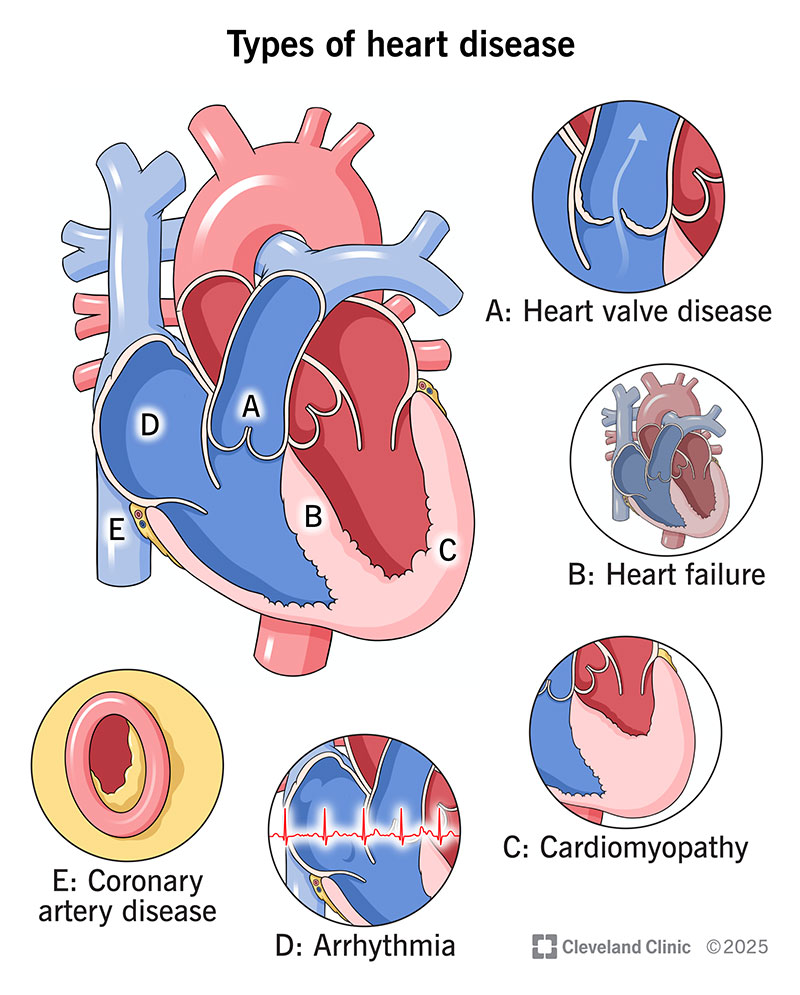
Heart Disease: Symptoms & Causes
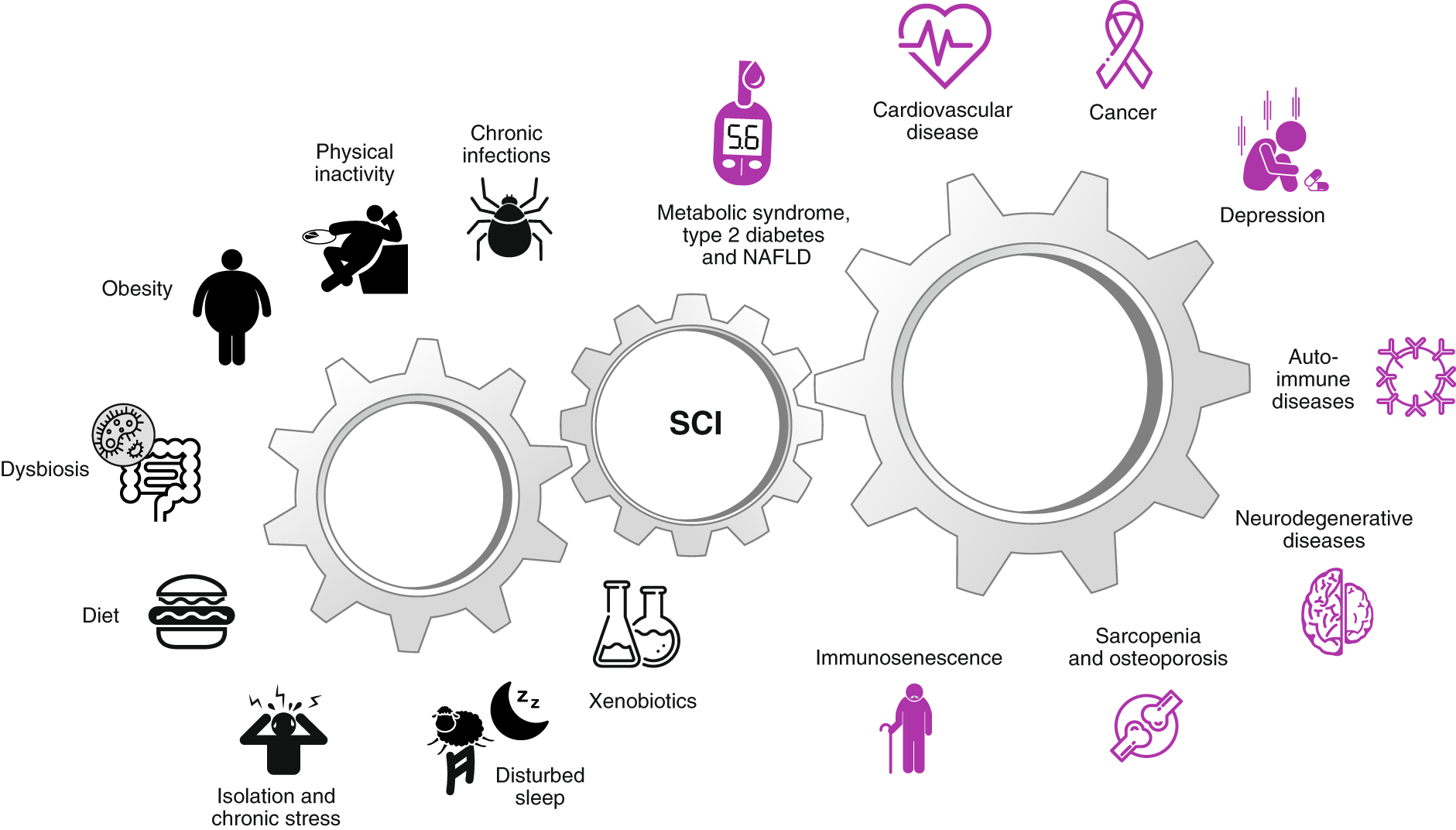
Chronic inflammation in the etiology of disease across the life span
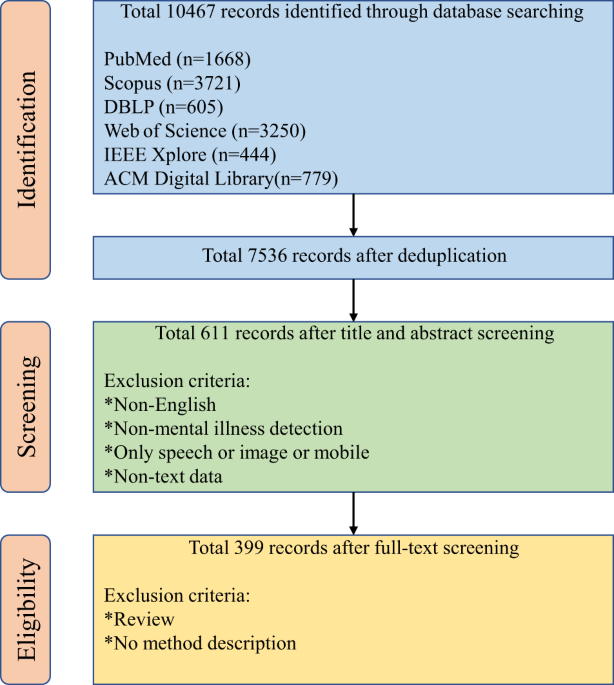
Natural language processing applied to mental illness detection: a narrative review

National Organization for Rare Disorders

Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015 - The Lancet
All CDs are intact, no scratches.

The Autoimmune Solution: Prevent and Reverse the Full Spectrum of Inflammatory Symptoms and Diseases
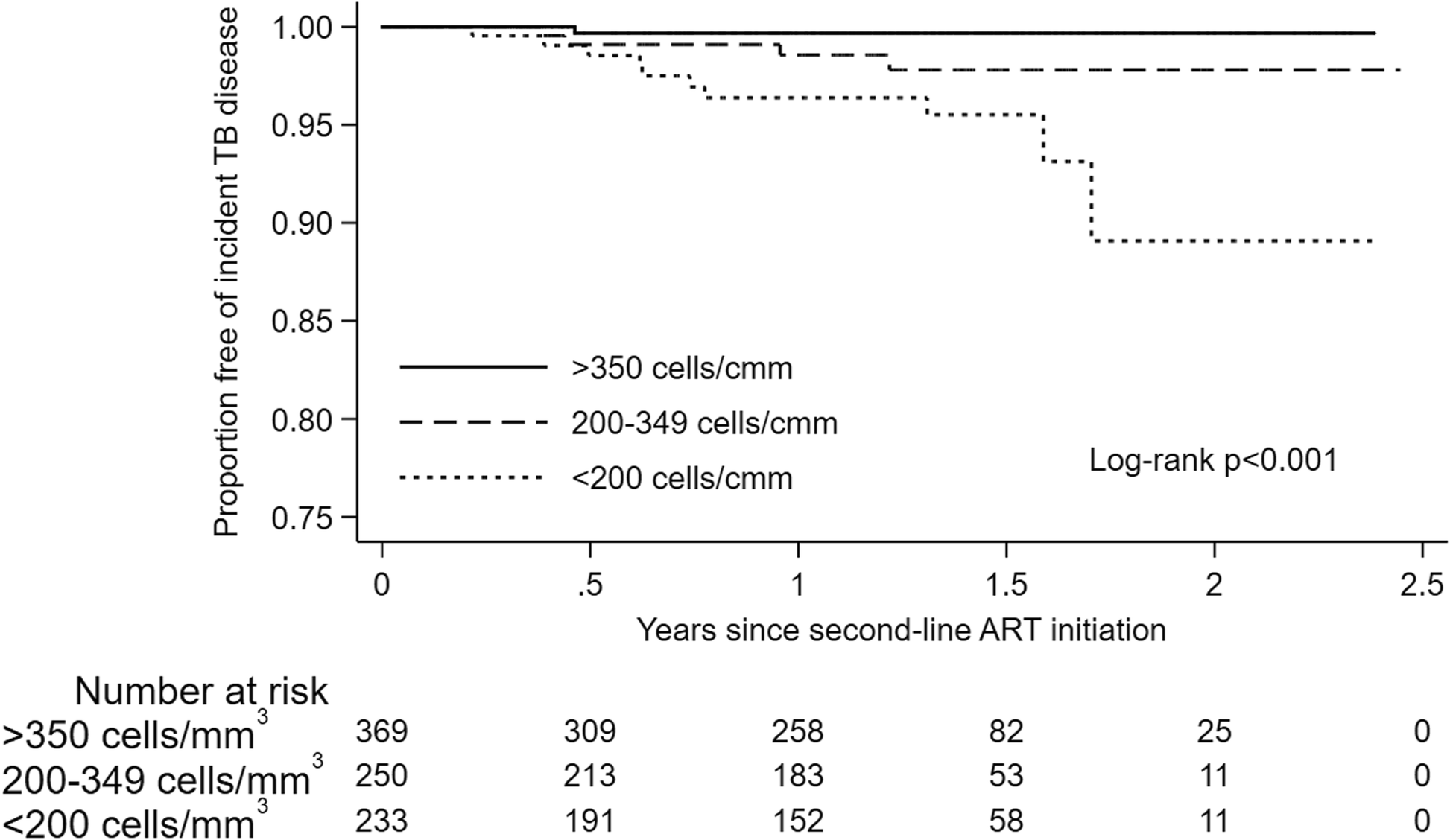
Incidence of tuberculosis in HIV-infected adults on first- and second-line antiretroviral therapy in India, BMC Infectious Diseases

Implementation of non-communicable disease policies from 2015 to 2020: a geopolitical analysis of 194 countries - The Lancet Global Health
Recomendado para você
-
Brain Test Game Level 287 to 304 Walkthrough, Brain Test Game Level 287 to 304, Brain Test Level 287, 288, 289, 290, 291, 292, 293, 294, 295, 296, 297, 298, 299, 300, 301, 302, 303, 304 Walkthrough, By Dangamevideos08 junho 2024
-
 حل Brain Test من المرحلة 280 إلى المرحلة 30008 junho 2024
حل Brain Test من المرحلة 280 إلى المرحلة 30008 junho 2024 -
 Brain Test Nivel 297 - ¡Sálvala!08 junho 2024
Brain Test Nivel 297 - ¡Sálvala!08 junho 2024 -
 Brain test 3 level 29708 junho 2024
Brain test 3 level 29708 junho 2024 -
 Brain Test Уровень 297 ответы (Спасите ее)08 junho 2024
Brain Test Уровень 297 ответы (Спасите ее)08 junho 2024 -
 Brain Test Level 297 (NEW) Uh! Something is wrong here Answer08 junho 2024
Brain Test Level 297 (NEW) Uh! Something is wrong here Answer08 junho 2024 -
 workflow4metabolomics (@workflow4metabo) / X08 junho 2024
workflow4metabolomics (@workflow4metabo) / X08 junho 2024 -
 Psychiatry International, Free Full-Text08 junho 2024
Psychiatry International, Free Full-Text08 junho 2024 -
 Frontiers Citrullination of Proteins as a Specific Response08 junho 2024
Frontiers Citrullination of Proteins as a Specific Response08 junho 2024 -
 Erythropoietin in traumatic brain injury (EPO-TBI): a double-blind08 junho 2024
Erythropoietin in traumatic brain injury (EPO-TBI): a double-blind08 junho 2024
você pode gostar
-
 CapCut_Nomes De Meninos Raros E Bonitos08 junho 2024
CapCut_Nomes De Meninos Raros E Bonitos08 junho 2024 -
 Infinite Dendrogram – Anime and me08 junho 2024
Infinite Dendrogram – Anime and me08 junho 2024 -
 How to get to Atelier do Ju Corte Real in Santo Amaro by Metro08 junho 2024
How to get to Atelier do Ju Corte Real in Santo Amaro by Metro08 junho 2024 -
 Enemy rooks are connected? No problem! Black to move : r/chess08 junho 2024
Enemy rooks are connected? No problem! Black to move : r/chess08 junho 2024 -
 Rodomaior Transportes08 junho 2024
Rodomaior Transportes08 junho 2024 -
 Advice? : r/Bloxburg08 junho 2024
Advice? : r/Bloxburg08 junho 2024 -
 Happy Birthday, Mizuha! (Just realized it while looking at the wiki) : r/HenSuki08 junho 2024
Happy Birthday, Mizuha! (Just realized it while looking at the wiki) : r/HenSuki08 junho 2024 -
 will roblox come to playstation|TikTok-sökning08 junho 2024
will roblox come to playstation|TikTok-sökning08 junho 2024 -
 Image result for eiffel tower images08 junho 2024
Image result for eiffel tower images08 junho 2024 -
CW Gotham Knights08 junho 2024

