Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome-related arterial vasculopathy and skeletal anomaly
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 09 junho 2024
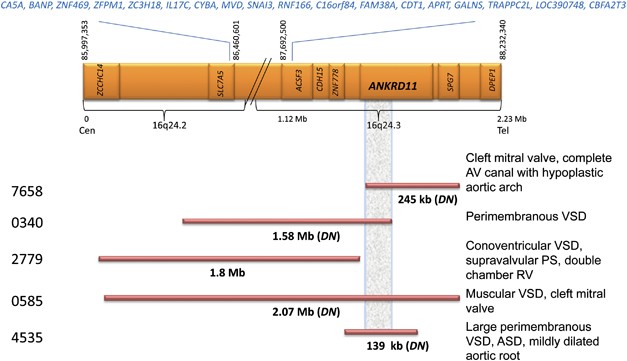
Rare DNA copy number variants in cardiovascular malformations with extracardiac abnormalities
Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome-related arterial vasculopathy and skeletal anomaly
Mutations in COL27A1 cause Steel syndrome and suggest a founder mutation effect in the Puerto Rican population
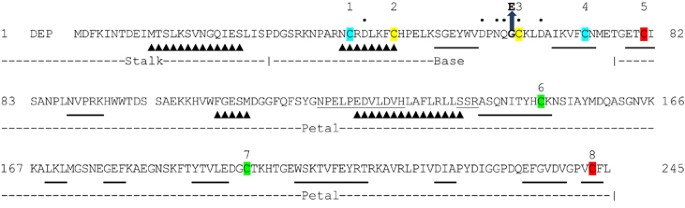
Vascular Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome in siblings with biallelic COL3A1 sequence variants and marked clinical variability in the extended family

PDF) Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome-related arterial vasculopathy and skeletal anomaly
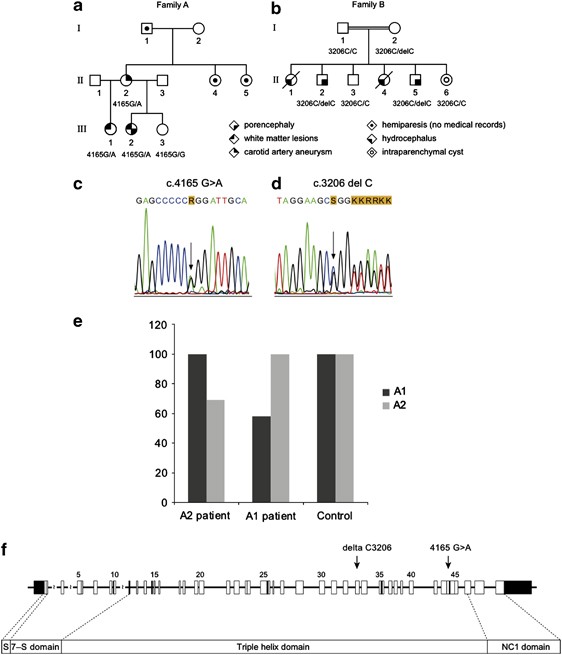
COL4A2 mutation associated with familial porencephaly and small-vessel disease

Genetic Basis for Congenital Heart Disease: Revisited: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association

Nervous system defects in the ep300 morphant zebrafish reveals new

Main clinical signs of the thirty-one Italian RSTS patients.

Protein-protein interaction network describes the possible interaction
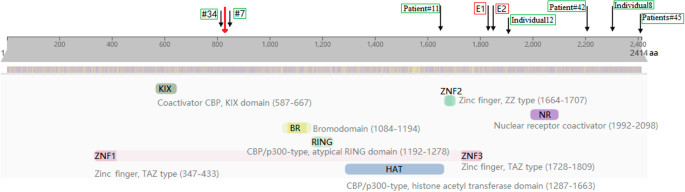
Case report: a Chinese girl like atypical Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome caused by a novel heterozygous mutation of the EP300 gene, BMC Medical Genomics

Effect of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) on the contraction
Recomendado para você
-
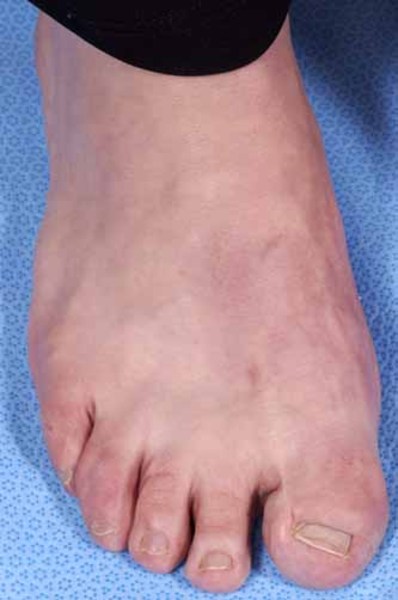 Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: MedlinePlus Genetics09 junho 2024
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: MedlinePlus Genetics09 junho 2024 -
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome 109 junho 2024
-
 Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf09 junho 2024
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf09 junho 2024 -
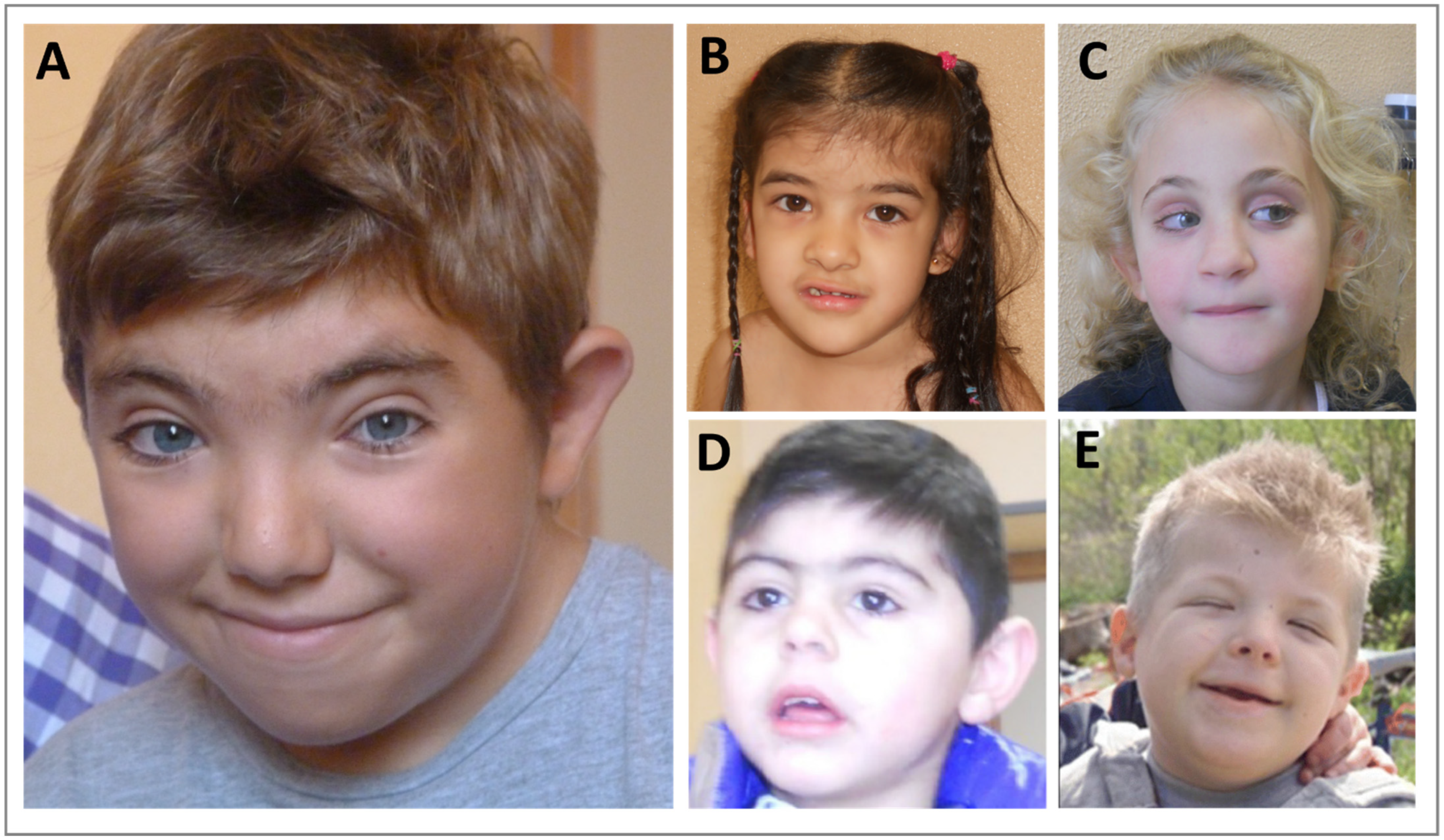 Genes, Free Full-Text09 junho 2024
Genes, Free Full-Text09 junho 2024 -
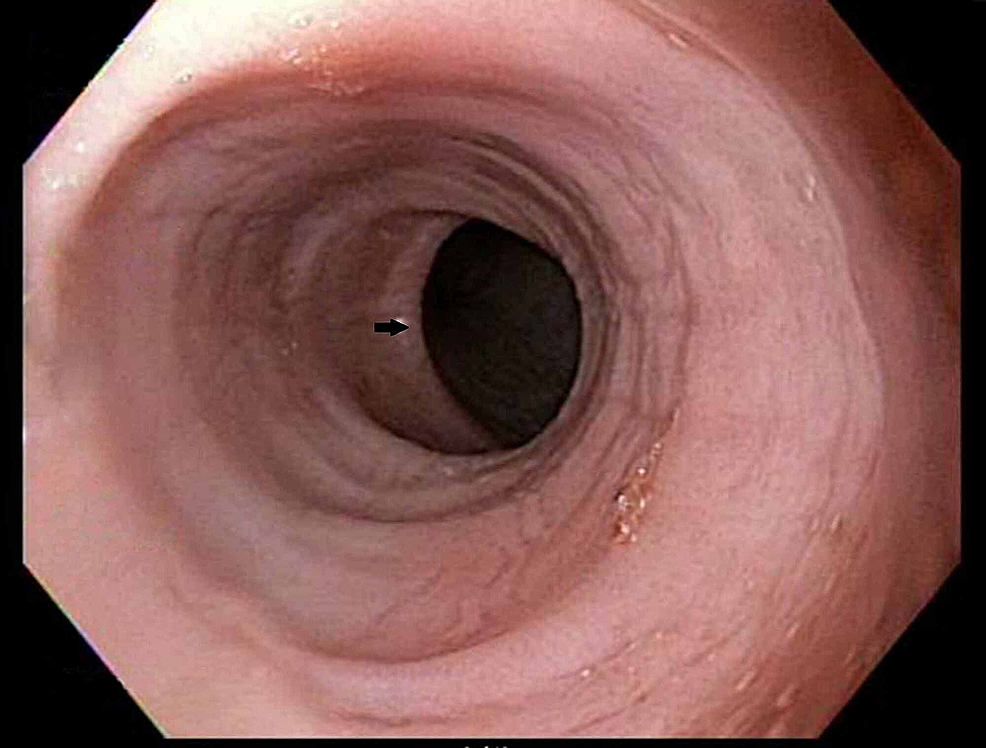 Cureus Barrett's Esophagus in Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome09 junho 2024
Cureus Barrett's Esophagus in Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome09 junho 2024 -
 genereviews.org - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf09 junho 2024
genereviews.org - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf09 junho 2024 -
 Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome in diverse populations - Tekendo‐Ngongang - 2020 - American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A - Wiley Online Library09 junho 2024
Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome in diverse populations - Tekendo‐Ngongang - 2020 - American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A - Wiley Online Library09 junho 2024 -
 Expanding the phenotype associated to KMT2A variants: overlapping09 junho 2024
Expanding the phenotype associated to KMT2A variants: overlapping09 junho 2024 -
 SciELO - Brasil - Prosthetic rehabilitation of a child with Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome after dental trauma: case report Prosthetic rehabilitation of a child with Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome after dental trauma: case report09 junho 2024
SciELO - Brasil - Prosthetic rehabilitation of a child with Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome after dental trauma: case report Prosthetic rehabilitation of a child with Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome after dental trauma: case report09 junho 2024 -
 Approach to inherited hypertrichosis: A brief review - Indian09 junho 2024
Approach to inherited hypertrichosis: A brief review - Indian09 junho 2024
você pode gostar
-
 VENOM FRUIT SHOWCASE (One Fruit Simulator)09 junho 2024
VENOM FRUIT SHOWCASE (One Fruit Simulator)09 junho 2024 -
 Horupitia Aholting, The Gamer Wiki09 junho 2024
Horupitia Aholting, The Gamer Wiki09 junho 2024 -
Jornais, televisão, redes sociais: que informação consomem os comentadores televisivos para analisar a guerra de Israel contra o Hamas? - Expresso09 junho 2024
-
 Com novo protagonista, Hades II terá textos em PT-BR09 junho 2024
Com novo protagonista, Hades II terá textos em PT-BR09 junho 2024 -
 Arena das Dunas - O palco das grandes emoções09 junho 2024
Arena das Dunas - O palco das grandes emoções09 junho 2024 -
 Menhera Chan Kawaii Badge Soft Button Lapel Pin Decor Brooch Jewelry Decoration Gift 58mm09 junho 2024
Menhera Chan Kawaii Badge Soft Button Lapel Pin Decor Brooch Jewelry Decoration Gift 58mm09 junho 2024 -
 Scp-001, SCP FOUNDATION SCPs Wiki09 junho 2024
Scp-001, SCP FOUNDATION SCPs Wiki09 junho 2024 -
 That 'AI-Generated' Anime Is Pissing Off Professional Animators09 junho 2024
That 'AI-Generated' Anime Is Pissing Off Professional Animators09 junho 2024 -
 ROBLOX LEGO Ideas Building Contest09 junho 2024
ROBLOX LEGO Ideas Building Contest09 junho 2024 -
 Papa's Hot Doggeria HD - Thanksgiving Season09 junho 2024
Papa's Hot Doggeria HD - Thanksgiving Season09 junho 2024
