Mean platelet volume levels in children with sleep-disordered
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 16 maio 2024
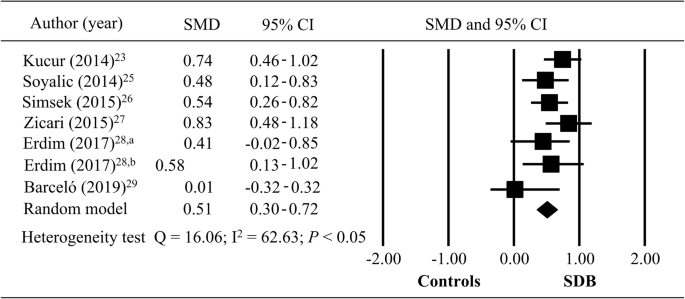
Background Pediatric sleep-disordered breathing (SDB) correlated with respiratory conditions of snoring and hypopnea. Mean platelet volume (MPV) was an inflammatory marker, related to increased inflammatory condition of pediatric patients. Increase of MPV level may cause failure to thrive or increased upper airway infection rate. The aim of this study was to perform systematic review and meta-analysis to investigate the difference on MPV values for pediatric SDB, and compare the change on MPV after surgery in patients with pediatric SDB. Methods A systemic review of the studies from PubMed, EMBASE, and Cochrane Library databases was conducted in March 2020, supported by reviewing of published articles for studies comparing MPV in pediatric SDB. Meta-analysis was used to compare the change of MPV in pediatric SDB, and sub-group analysis was also used to compare the MPV decrease after surgeries of adenoidectomy or adenotonsillectomy. Results There were seven studies included in the review. Six of them including 963 subjects showed that a significant increase of MPV was noted in pediatric SDB compared to those in pediatric non-SDB (P < 0.05). Total standardized mean difference (SMD) in MPV between pediatric SDB and non-SDB was 0.51 (95% CI =0.30–0.72, P < 0.05). A significant decrease of MPV was found in pediatric SDB patients who underwent surgery (total SMD = − 0.36; 95% CI = − 0.70– -0.02, P < 0.05). Decreases of MPV after adenoidectomy and adenotonsillectomy were observed, but only the effect of adenotonsillectomy had a statistical significance (total SMD = − 0.72; 95% CI = − 1.18 – -0.26, P < 0.05). Conclusion The MPV was significantly higher in patients with pediatric SDB, indicating the presence of increased platelet activity in pediatric SDB patients. The level of MPV could be reduced by the two surgeries, especially adenotonsillectomy.

The Biotoxin Pathway & CIRS Diagnosis

Full article: Mean Platelet Volume and Platelet Distribution Width in non-diabetic subjects with Obstructive Sleep Apnoea Syndrome: New indices of severity?

Cardiovascular Complications of Down Syndrome: Scoping Review and Expert Consensus

Micronutrients for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Youths: A Placebo-Controlled Randomized Clinical Trial - Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry
Mean Platelet Volume and Arterial Stiffness – Clinical Relationship and Common Genetic Variability

Platelet disorders in children: A diagnostic approach - Israels - 2011 - Pediatric Blood & Cancer - Wiley Online Library
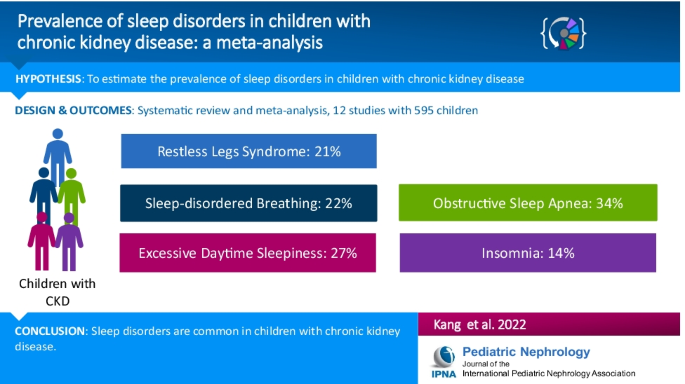
Prevalence of sleep disorders in children with chronic kidney disease: a meta-analysis

Mental Disorders - Hurdles of a Sound Mind
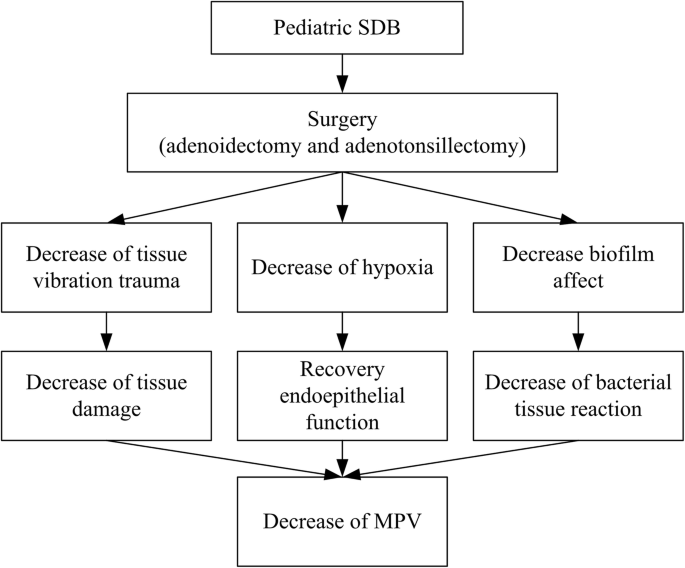
Mean platelet volume levels in children with sleep-disordered breathing: a meta-analysis, BMC Pediatrics
IJMS, Free Full-Text

High mean platelet volume-to-platelet count ratio as a diagnostic maker for increased risk of liver function damage in pediatric patients with infectious mononucleosis in China.

A meta‐analysis: Does vitamin D play a promising role in sleep disorders? - Yan - 2020 - Food Science & Nutrition - Wiley Online Library
Recomendado para você
-
 Download Kipas Guys 0.41.1 for Android16 maio 2024
Download Kipas Guys 0.41.1 for Android16 maio 2024 -
 FINALMENTE 😱 NOVA ATUALIZAÇÃO 0.41 DO STUMBLE GUYS 😱16 maio 2024
FINALMENTE 😱 NOVA ATUALIZAÇÃO 0.41 DO STUMBLE GUYS 😱16 maio 2024 -
 👑como baixar stumble guys block dash infinito 0.41.1!16 maio 2024
👑como baixar stumble guys block dash infinito 0.41.1!16 maio 2024 -
 Stumble Guys 0.41.1 versão oficial - Dluz Games16 maio 2024
Stumble Guys 0.41.1 versão oficial - Dluz Games16 maio 2024 -
![PDF] Investigating the effect of extended high-frequency hearing](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/a5446db56727d62565a493a75765098b773f9f07/6-Table2-1.png) PDF] Investigating the effect of extended high-frequency hearing16 maio 2024
PDF] Investigating the effect of extended high-frequency hearing16 maio 2024 -
 Impact of Treatment for Nasal Cavity Disorders on Sleep Quality16 maio 2024
Impact of Treatment for Nasal Cavity Disorders on Sleep Quality16 maio 2024 -
 Epidemiology and extracutaneous comorbidities of severe acne in16 maio 2024
Epidemiology and extracutaneous comorbidities of severe acne in16 maio 2024 -
 Quality of life in patients with persistent allergic rhinitis16 maio 2024
Quality of life in patients with persistent allergic rhinitis16 maio 2024 -
 Surgical anatomy of the external branch of the superior laryngeal16 maio 2024
Surgical anatomy of the external branch of the superior laryngeal16 maio 2024 -
 Effectiveness of corticosteroids in otitis media with effusion: an16 maio 2024
Effectiveness of corticosteroids in otitis media with effusion: an16 maio 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Honor of Kings android iOS apk download for free-TapTap16 maio 2024
Honor of Kings android iOS apk download for free-TapTap16 maio 2024 -
 Nuvem vermelha naruto png16 maio 2024
Nuvem vermelha naruto png16 maio 2024 -
 2010-11 League One preview – Who's going up and who's going down? – talkSPORT16 maio 2024
2010-11 League One preview – Who's going up and who's going down? – talkSPORT16 maio 2024 -
 Caixa com frutas do Demônio - One Piece16 maio 2024
Caixa com frutas do Demônio - One Piece16 maio 2024 -
:quality(75)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/elcomercio/EQSJ4LX7KZFA5NQSAP236P6N4U.jpg) Stranger Things Temporada 4 Parte 2 en Netflix: esta es la fecha y16 maio 2024
Stranger Things Temporada 4 Parte 2 en Netflix: esta es la fecha y16 maio 2024 -
 Hdhdhd - Animas - Book Online - Prices, Reviews, Photos16 maio 2024
Hdhdhd - Animas - Book Online - Prices, Reviews, Photos16 maio 2024 -
bom desenhista – Como desenhar anime16 maio 2024
-
Bolo pneu lindo no tema moto 🤩 Massa - marybolosedoces_ve16 maio 2024
-
 MOB Games - Poppy Playtime Ch. 1 (Original Game Soundtrack) Lyrics16 maio 2024
MOB Games - Poppy Playtime Ch. 1 (Original Game Soundtrack) Lyrics16 maio 2024 -
 Spider Solitaire Online - Free Play & No Download16 maio 2024
Spider Solitaire Online - Free Play & No Download16 maio 2024
