Extra high superoxide dismutase in host tissue is associated with
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 31 maio 2024
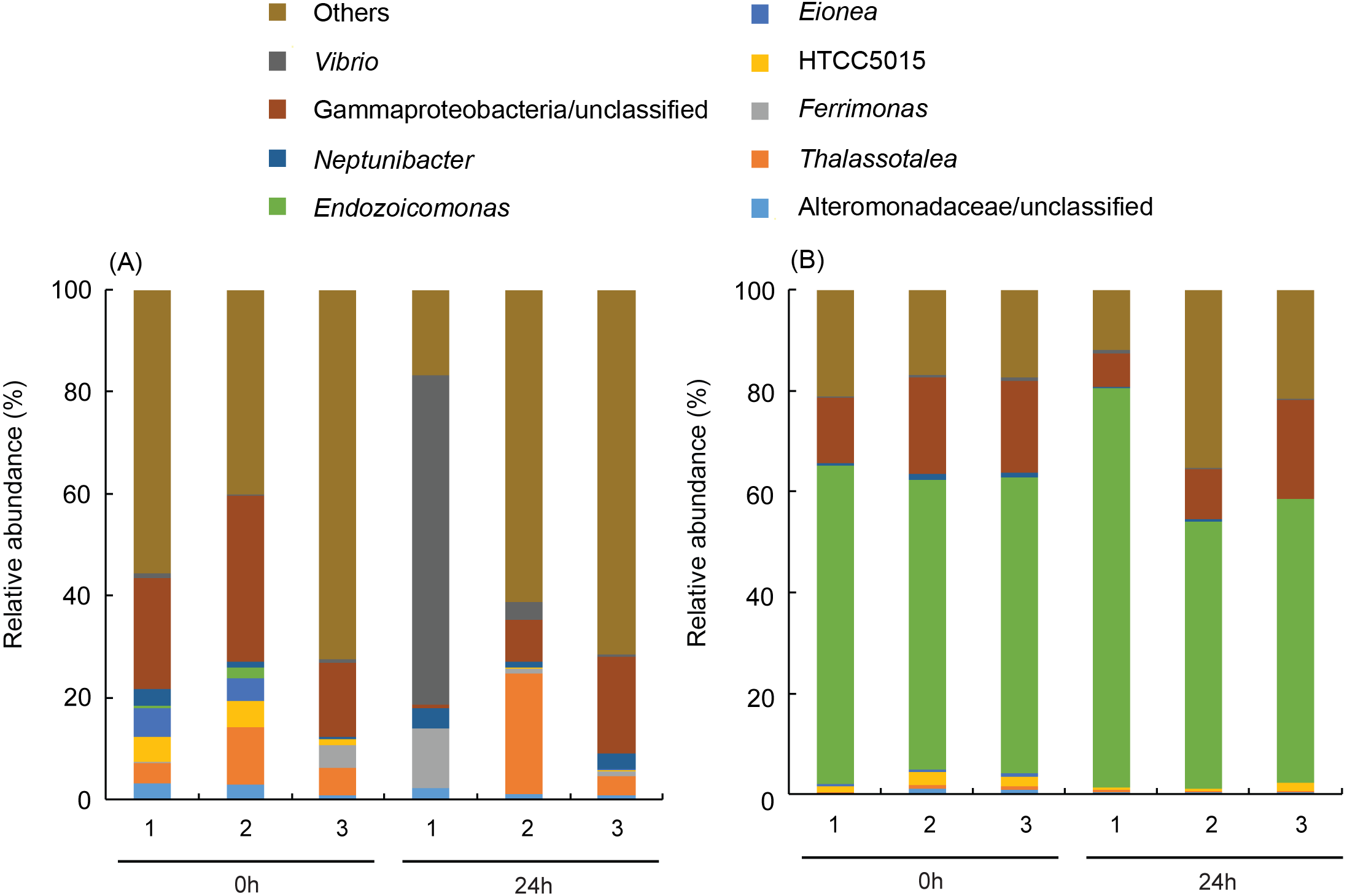
Global warming threatens reef-building corals with large-scale bleaching events; therefore, it is important to discover potential adaptive capabilities for increasing their temperature resistance before it is too late. This study presents two coral species (Platygyra verweyi and Isopora palifera) surviving on a reef having regular hot water influxes via a nearby nuclear power plant that exhibited completely different bleaching susceptibilities to thermal stress, even though both species shared several so-called “winner” characteristics (e.g., containing Durusdinium trenchii, thick tissue, etc.). During acute heating treatment, algal density did not decline in P. verweyi corals within three days of being directly transferred from 25 to 31 °C; however, the same treatment caused I. palifera to lose < 70% of its algal symbionts within 24 h. The most distinctive feature between the two coral species was an overwhelmingly higher constitutive superoxide dismutase (ca. 10-fold) and catalase (ca. 3-fold) in P. verweyi over I. palifera. Moreover, P. verweyi also contained significantly higher saturated and lower mono-unsaturated fatty acids, especially a long-chain saturated fatty acid (C22:0), than I. palifera, and was consistently associated with the symbiotic bacteria Endozoicomonas, which was not found in I. palifera. However, antibiotic treatment and inoculation tests did not support Endozoicomonas having a direct contribution to thermal resistance. This study highlights that, besides its association with a thermally tolerable algal symbiont, a high level of constitutive antioxidant enzymes in the coral host is crucial for coral survivorship in the more fluctuating and higher temperature environments.

Extra high superoxide dismutase in host tissue is associated with improving bleaching resistance in “thermal adapted” and Durusdinium trenchii-associating coral [PeerJ]

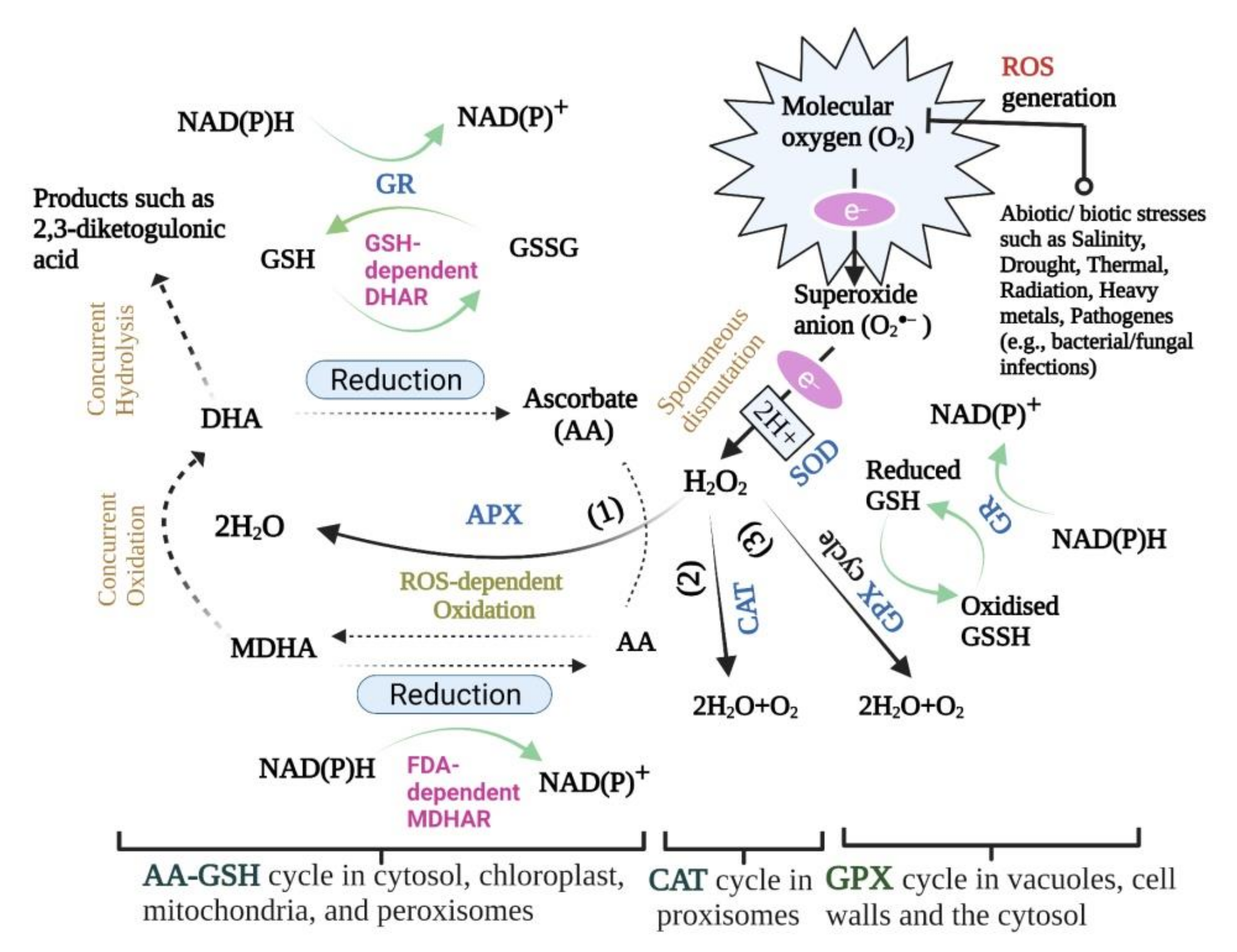
Antioxidant enzymes. The superoxide radical anion can be transformed
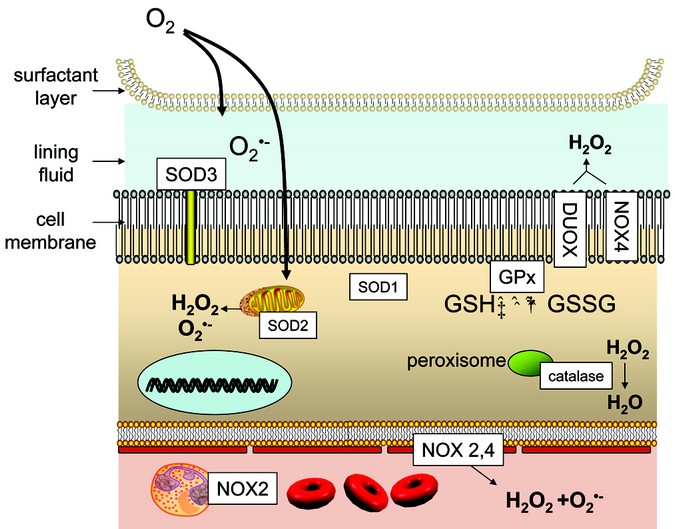
Oxygen Toxicity and Reactive Oxygen Species: The Devil Is in the Details
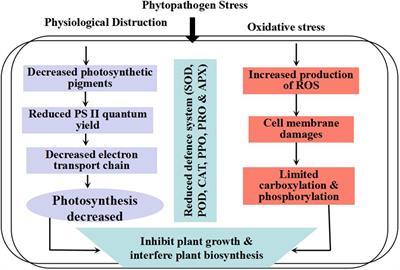
Frontiers ROS and Oxidative Response Systems in Plants Under Biotic and Abiotic Stresses: Revisiting the Crucial Role of Phosphite Triggered Plants Defense Response

Diquinol Functionality Boosts the Superoxide Dismutase Mimicry of a Zn(II) Complex with a Redox-Active Ligand while Maintaining Catalyst Stability and Enhanced Activity in Phosphate Solution
Biology, Free Full-Text

Molecular dynamics analysis of superoxide dismutase 1 mutations suggests decoupling between mechanisms underlying ALS onset and progression - Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal
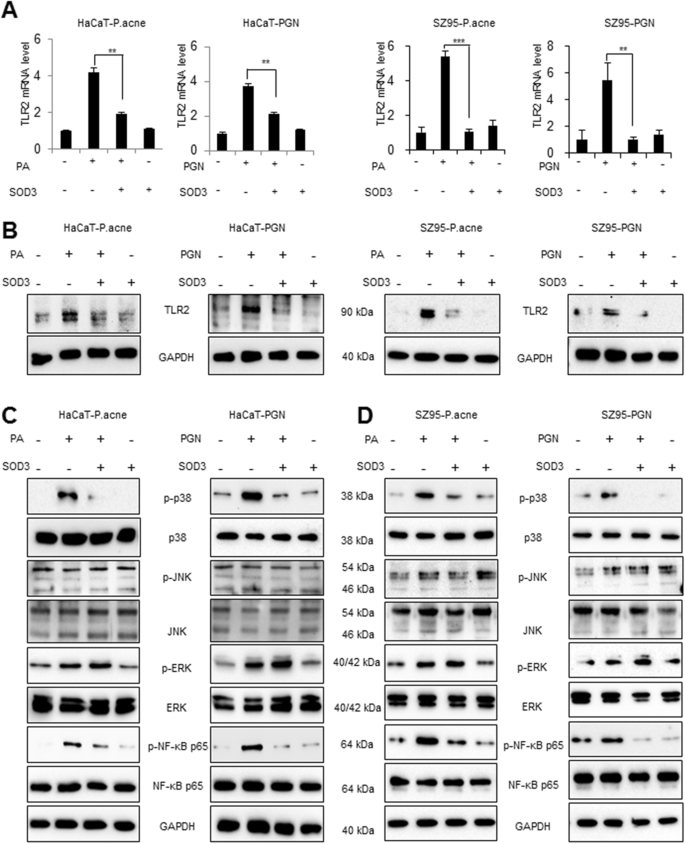
Inhibitory effects of superoxide dismutase 3 on Propionibacterium acnes-induced skin inflammation
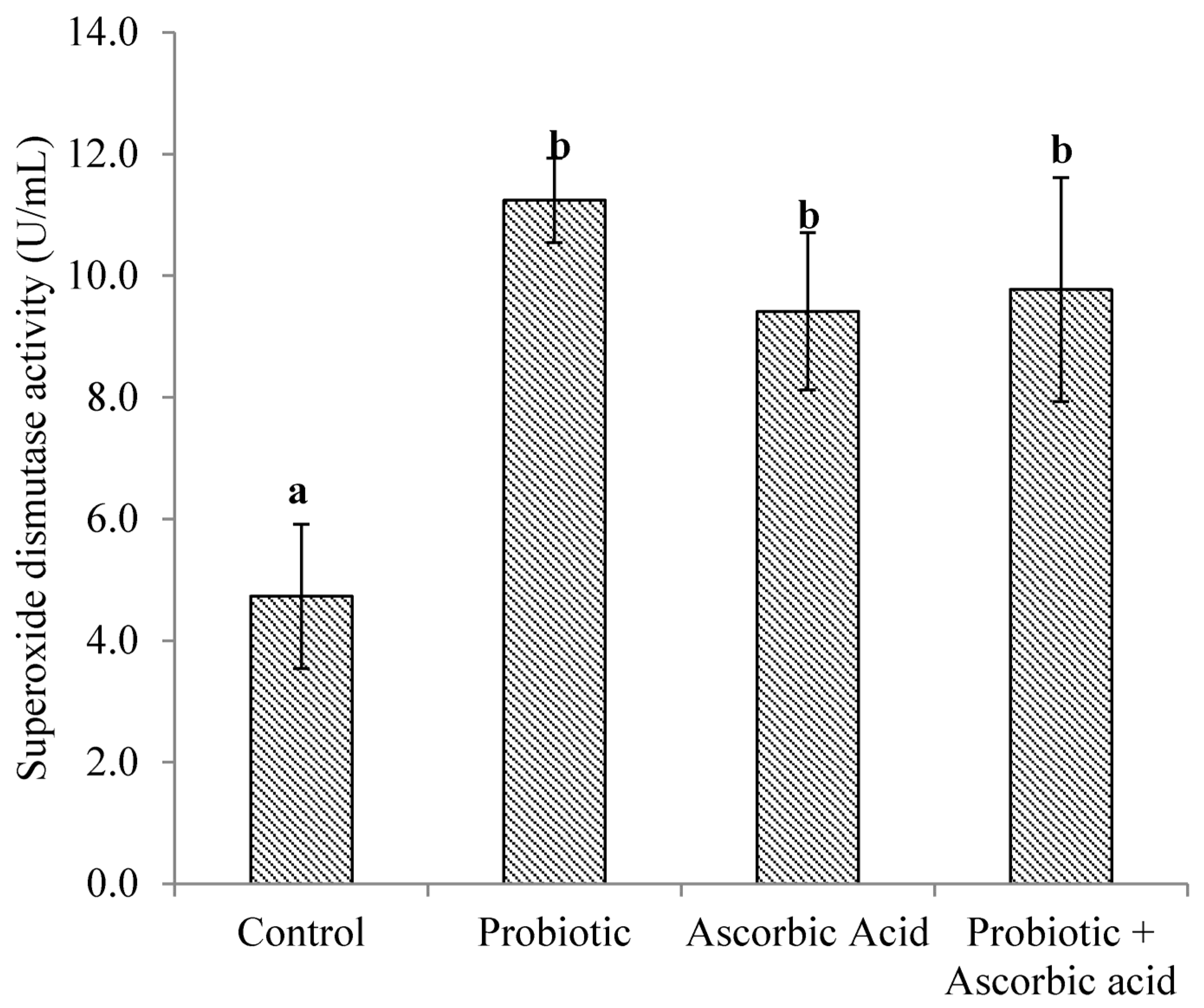
Animals, Free Full-Text
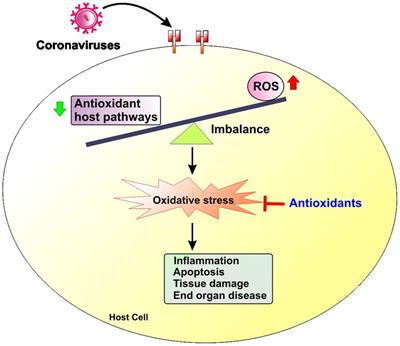
Frontiers The role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of infections with coronaviruses
Recomendado para você
-
 FAST TIME LOG- SINALIZADOR VAGA LOGISTICO - NEW Sistemas e31 maio 2024
FAST TIME LOG- SINALIZADOR VAGA LOGISTICO - NEW Sistemas e31 maio 2024 -
 Auxiliar Ambiental, Fortaleza – CE, 01 vaga(s)31 maio 2024
Auxiliar Ambiental, Fortaleza – CE, 01 vaga(s)31 maio 2024 -
 Hospital Tacchini abre 62 vagas de trabalho para equipe de31 maio 2024
Hospital Tacchini abre 62 vagas de trabalho para equipe de31 maio 2024 -
 Assistente de Monitoramento e Avaliação - Plan Internacional31 maio 2024
Assistente de Monitoramento e Avaliação - Plan Internacional31 maio 2024 -
 PathWave BenchVue Software31 maio 2024
PathWave BenchVue Software31 maio 2024 -
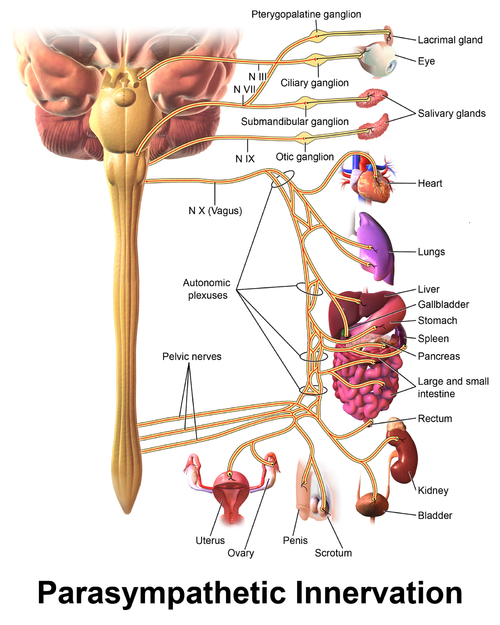 Vagus Nerve - Physiopedia31 maio 2024
Vagus Nerve - Physiopedia31 maio 2024 -
 Trabalhe conosco - Segvap31 maio 2024
Trabalhe conosco - Segvap31 maio 2024 -
 Your vegus nerve and constipation - 7 ways to help31 maio 2024
Your vegus nerve and constipation - 7 ways to help31 maio 2024 -
 2022 Georgia Tech Football Information Guide by GTAthletics - Issuu31 maio 2024
2022 Georgia Tech Football Information Guide by GTAthletics - Issuu31 maio 2024 -
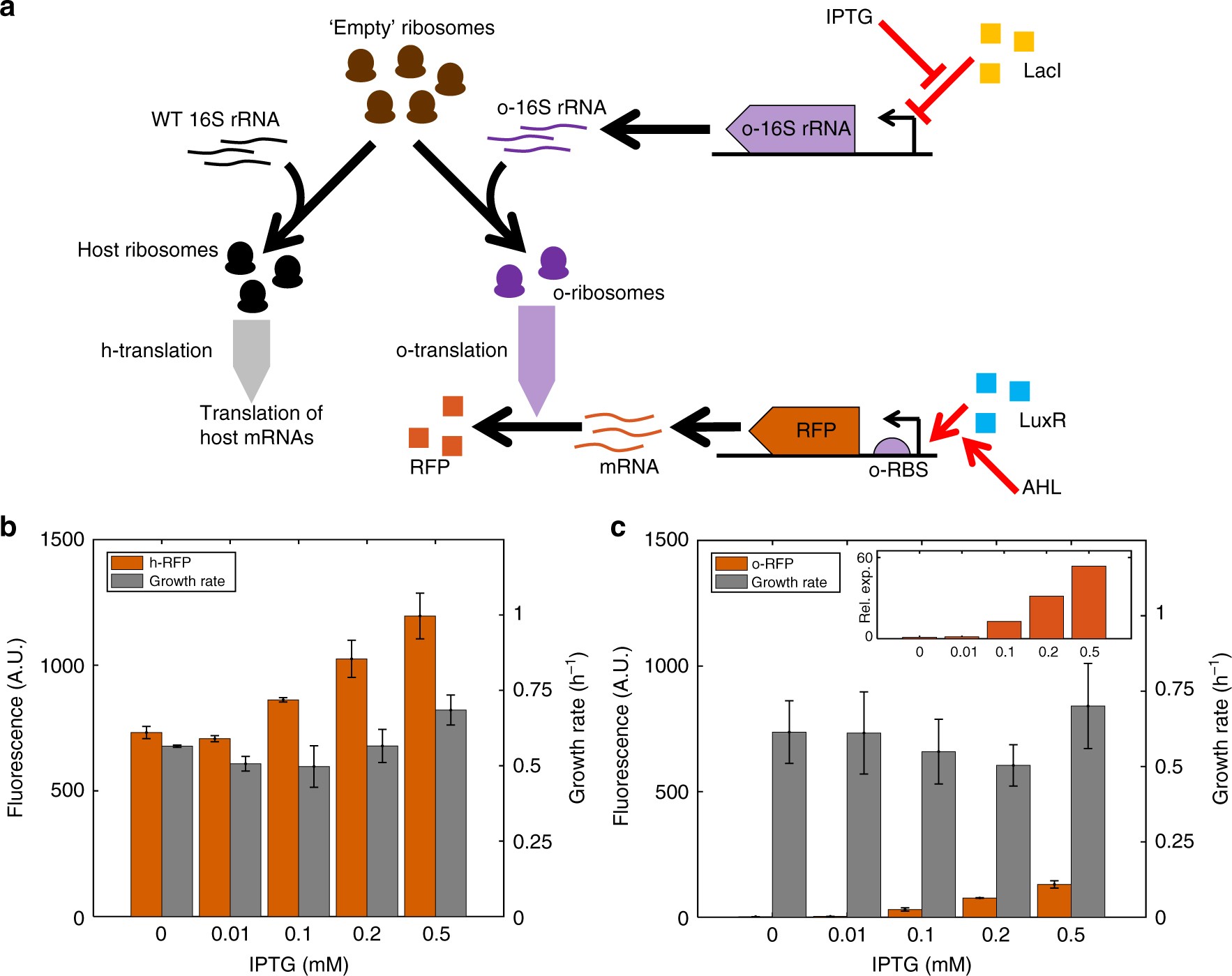 Dynamic allocation of orthogonal ribosomes facilitates uncoupling31 maio 2024
Dynamic allocation of orthogonal ribosomes facilitates uncoupling31 maio 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Fable II – Many Cool Things31 maio 2024
Fable II – Many Cool Things31 maio 2024 -
 The CBD Expert Series: From Masterchef to Cannabis Chef with Nick Nappi31 maio 2024
The CBD Expert Series: From Masterchef to Cannabis Chef with Nick Nappi31 maio 2024 -
 Big Poster do Anime Fullmetal Alchemist - 90x60 cm - LO02731 maio 2024
Big Poster do Anime Fullmetal Alchemist - 90x60 cm - LO02731 maio 2024 -
 Papel de Parede All Kids Xadrez Amarelo e Rosa H2910807 - Rolo31 maio 2024
Papel de Parede All Kids Xadrez Amarelo e Rosa H2910807 - Rolo31 maio 2024 -
 Conjunto de Mesa 4 Cadeiras Plastico Inovar Cestaplus Branca31 maio 2024
Conjunto de Mesa 4 Cadeiras Plastico Inovar Cestaplus Branca31 maio 2024 -
 Valorant coaches and players unhappy with planned Pearl and31 maio 2024
Valorant coaches and players unhappy with planned Pearl and31 maio 2024 -
 sem ideia de live, ent vamos conversar um pouquinho :D31 maio 2024
sem ideia de live, ent vamos conversar um pouquinho :D31 maio 2024 -
 Multiple Voice Actors Discuss Becoming Kratos in God of War Ragnarok Dev Diary31 maio 2024
Multiple Voice Actors Discuss Becoming Kratos in God of War Ragnarok Dev Diary31 maio 2024 -
 Estrella (strellyta2130) - Profile31 maio 2024
Estrella (strellyta2130) - Profile31 maio 2024 -
 Coleção Cinderela - Vestido de Noiva RJ31 maio 2024
Coleção Cinderela - Vestido de Noiva RJ31 maio 2024