Differential cellular stiffness contributes to tissue elongation on an expanding surface
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 31 maio 2024


Vaginal Fibroblast Behavior as a Function of Stiffness Changes in a Polyisocyanide Hydrogel for Prolapse Repair
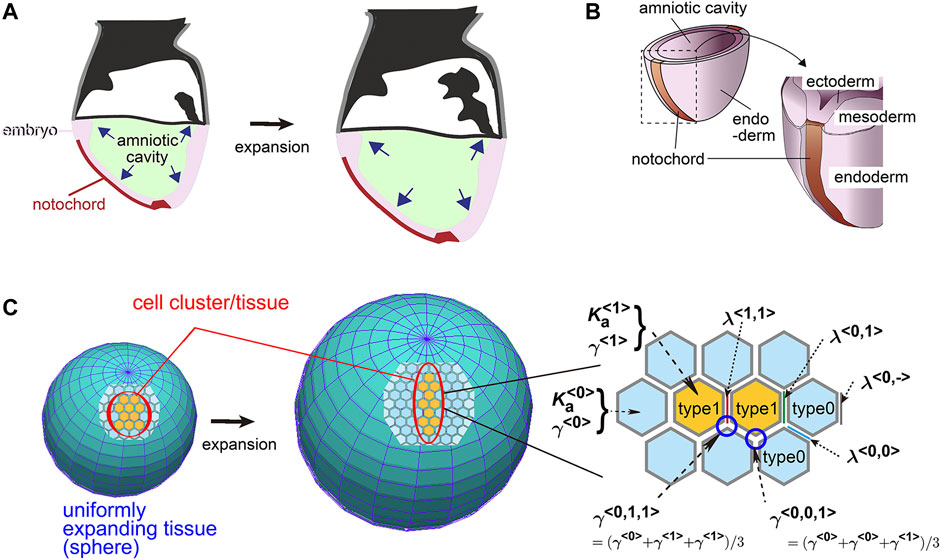
Frontiers Differential Cellular Stiffness Contributes to Tissue Elongation on an Expanding Surface

Spreading of cells correlates with hydrogel stiffness. (A) Phase

Expansin-mediated developmental and adaptive responses: A matter of cell wall biomechanics?, Quantitative Plant Biology
Frontiers Differential Cellular Stiffness Contributes to Tissue Elongation on an Expanding Surface

Transducing compressive forces into cellular outputs in cancer and beyond

An overview of substrate stiffness guided cellular response and its applications in tissue regeneration - ScienceDirect

Surface Roughness and Substrate Stiffness Synergize To Drive Cellular Mechanoresponse

Cellular segregation in cocultures is driven by differential adhesion and contractility on distinct timescales
Frontiers Stem Cell Mechanobiology and the Role of Biomaterials in Governing Mechanotransduction and Matrix Production for Tissue Regeneration
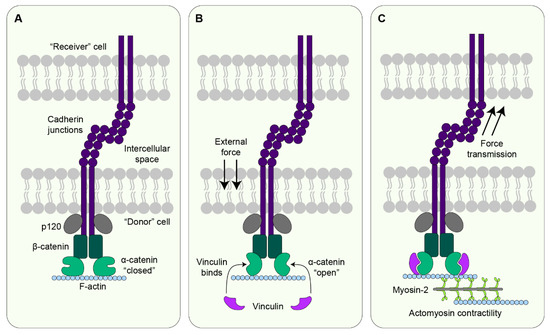
JDB, Free Full-Text

An overview of substrate stiffness guided cellular response and its applications in tissue regeneration - ScienceDirect

Cellular Heterogeneity in Pressure and Growth Emerges from Tissue Topology and Geometry - ScienceDirect
Recomendado para você
-
 Cute Chiko chicken to light up your keyboard >o< Anyone like these little pastel keycaps? 🙋♀️ : r/MechanicalKeyboards31 maio 2024
Cute Chiko chicken to light up your keyboard >o< Anyone like these little pastel keycaps? 🙋♀️ : r/MechanicalKeyboards31 maio 2024 -
 Blue Cell Phone Squishies for sale31 maio 2024
Blue Cell Phone Squishies for sale31 maio 2024 -
 Big Chic Novelty Keycaps Gaming Accessories Mechanical Keyboard Keycap Personality Design Cartoon Cherry MX Axis Anim Keycap (Single R4 Keys (KIT 1) : Electronics31 maio 2024
Big Chic Novelty Keycaps Gaming Accessories Mechanical Keyboard Keycap Personality Design Cartoon Cherry MX Axis Anim Keycap (Single R4 Keys (KIT 1) : Electronics31 maio 2024 -
:format(jpeg)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/52104725/IMG_1128.0.0.jpeg) Best mechanical keyboards of 2016 - Polygon31 maio 2024
Best mechanical keyboards of 2016 - Polygon31 maio 2024 -
edit for u played (Jessie Murph)31 maio 2024
-
 why am i so squishy 😭 😭 : r/HypixelSkyblock31 maio 2024
why am i so squishy 😭 😭 : r/HypixelSkyblock31 maio 2024 -
The cosy autumnal crossword31 maio 2024
-
 Moneybagg Yo U Played (Live Piano Version)31 maio 2024
Moneybagg Yo U Played (Live Piano Version)31 maio 2024 -
 Viewfinder vs capturing a photo in Whatsapp on Xiaomi EU 12.5.19 - POCO F3. Any one facing the same issue? It always adds more space to the right side : r/PocoPhones31 maio 2024
Viewfinder vs capturing a photo in Whatsapp on Xiaomi EU 12.5.19 - POCO F3. Any one facing the same issue? It always adds more space to the right side : r/PocoPhones31 maio 2024 -
 Boy Squishies31 maio 2024
Boy Squishies31 maio 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Conjunto De ícones De Giz Branco Para Um Salão De Tatuagem E31 maio 2024
Conjunto De ícones De Giz Branco Para Um Salão De Tatuagem E31 maio 2024 -
 Dragon Age: Origins walkthrough: Page 731 maio 2024
Dragon Age: Origins walkthrough: Page 731 maio 2024 -
 ✨Articuno+Zapdos+Moltres GALAR Shiny 6IV✨ Pokemon Scarlet & Violet 3-PACK FAST31 maio 2024
✨Articuno+Zapdos+Moltres GALAR Shiny 6IV✨ Pokemon Scarlet & Violet 3-PACK FAST31 maio 2024 -
 10 Best Features In Suicide Squad: Kill The Justice League31 maio 2024
10 Best Features In Suicide Squad: Kill The Justice League31 maio 2024 -
 Is Rate my tactic making sense? : r/footballmanagergames31 maio 2024
Is Rate my tactic making sense? : r/footballmanagergames31 maio 2024 -
Cenário Transparente31 maio 2024
-
 Subway Surfers: Halloween, Subway Surfers Wiki BR31 maio 2024
Subway Surfers: Halloween, Subway Surfers Wiki BR31 maio 2024 -
 Five Nights at Toy Freddy's Series : RickyG : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive31 maio 2024
Five Nights at Toy Freddy's Series : RickyG : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive31 maio 2024 -
 Regionalização do Brasil: quais as diferentes regiões do Brasil31 maio 2024
Regionalização do Brasil: quais as diferentes regiões do Brasil31 maio 2024 -
 PARTIZAN OPET OD 0:2 DO POBEDE! Crno-beli uz penal u 93. minutu31 maio 2024
PARTIZAN OPET OD 0:2 DO POBEDE! Crno-beli uz penal u 93. minutu31 maio 2024

